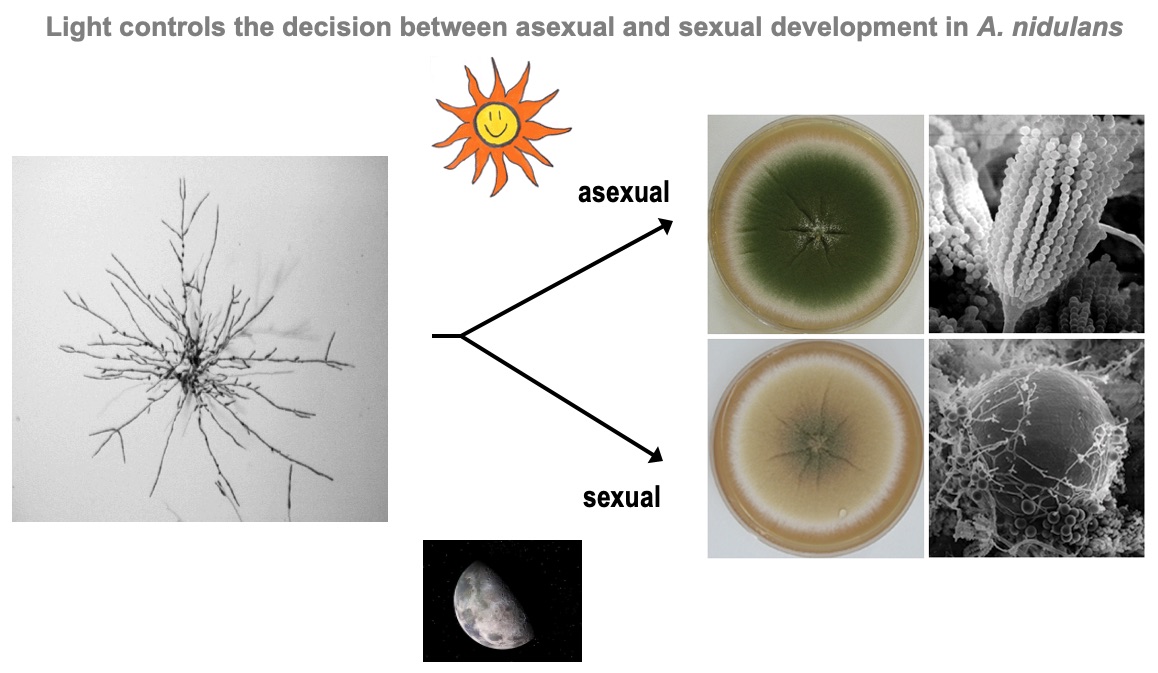
It was well known that Aspergillus nidulans responds to red light. The discovery of phytochrome started with a bet in the lab when we were searching for a new subject for a Diploma thesis. At that time, in 2004, we were invovled in the annotation of the genome and Kay Vienken found a sequence in the genome with similarity to plant phytochrome. He suggested that we follow that discovery. I suggested a more "safe" project on a kinase protein and we bet which project would be more successful. Well, the phytochrome indeed turned out to be THE red-light sensor in A. nidulans and we are working very successfully on that since then.
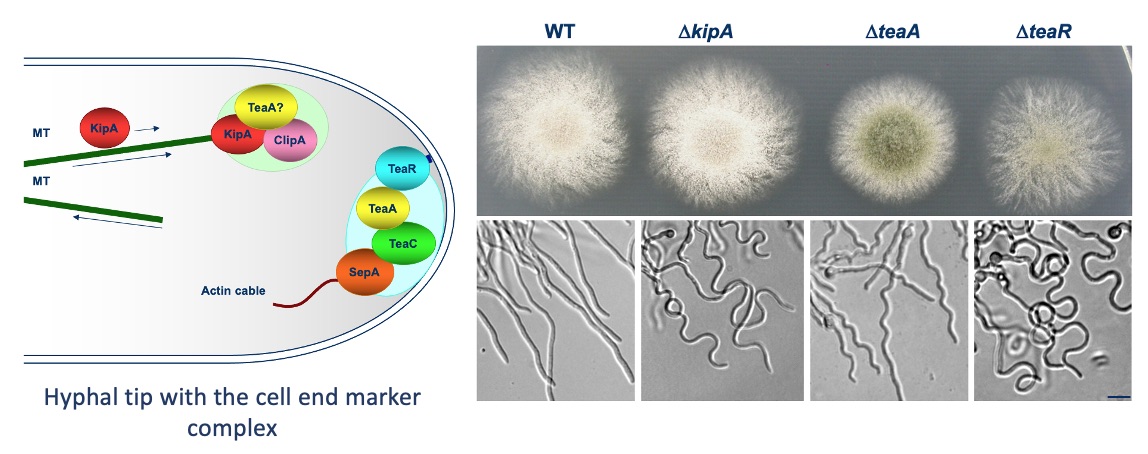
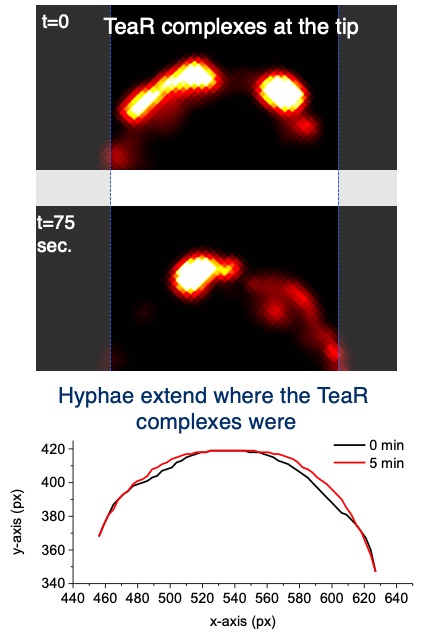
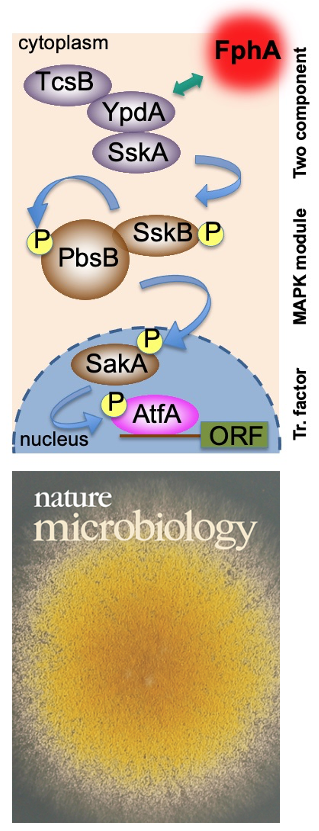
After the characterization of the gene in A. nidulans and the expression of the phytochrome protein in E. coli, we analyzed the signal transduction cascade and discovered that phytochrome has a cytoplasmic and a nuclear function. In the nucleus it interacts with the blue-light receptor LreA and the transcription factor VeA. The cytoplasmic function was discovered in a forward genetics approach, where we isolated "blind" mutants. Whole genome sequencing of one of the mutant revealed a mutation in the MAP kinase HogA (SakA). This was a great discovery, because it showed that light and stress sensing is related. This explained also the role for light sensing in nature.
Blumenstein, A., Vienken, K., Tasler, R., Purschwitz, J., Veith, D., Frankenberg-Dinkel, N. & Fischer, R. (2005) The Aspergillus nidulans phytochrome FphA represses sexual development in red light. Curr. Biol., 15:1833-1838.
Purschwitz, J., Müller, S., Kastner, C., Schöser, M., Haas, H., Espeso, E.A., Atoui, A., Calvo, A.M. & Fischer, R. (2008) Functional and physical interaction of blue and red-light sensors in Aspergillus nidulans. Curr. Biol., 18:255-259.
Hedtke, M., Rauscher, S., Röhrig ,J., Rodriguez, J., Yu, Z., & Fischer, R. (2015) Light-dependent gene activation in Aspergillus nidulans is strictly dependent on phytochrome and involves the interplay of phytochrome and white-collar-regulated histone H3 acetylation. Mol. Microbiol., 97:733-745.
Rauscher, S., Pacher, S., Kniemeyer, O. & Fischer, R. (2016) A phosphorylation code of the Aspergillus nidulans global regulator VelvetA (VeA) determines specific functions. Mol. Microbiol., 99:909-924.
Yu, Z., Armant, O. & Fischer, R. (2016) Fungi use the SakA/HogA pathway for phytochrome-dependent light signaling. Nature Microbiol., 2016, 1: 16019.
Yu, Z. & Fischer, R. (2019) Light sensing and responses in fungi. Nat. Rev. Microbiol., 17(1):25-36.